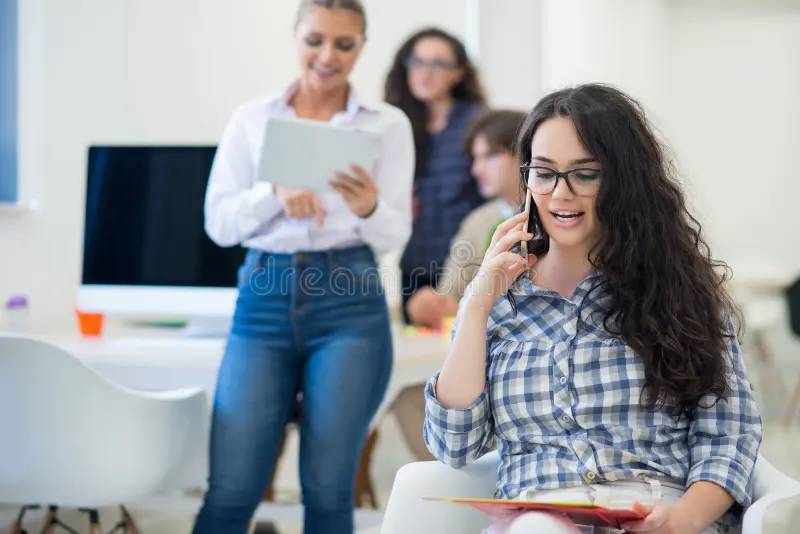
How does Blockchain work?
Blockchain technology works by grouping transactions into blocks. Each block is linked to the previous one, creating a chain of blocks, hence the name. Every transaction is verified and encrypted before being added to the chain, making it nearly impossible to alter once it’s recorded.
-
Transaction Initiation:
A transaction begins when one party creates and sends a request to the blockchain network. This request typically includes details such as the amount to be transferred, the recipient's address, and other relevant data. The transaction is then broadcasted to the network, where it awaits verification and validation by participating nodes.
-
Validation:
After a transaction is initiated, network nodes (the participants in the blockchain) work to verify its validity. These nodes check the transaction against predefined rules, ensuring it meets necessary conditions such as correct signatures, sufficient funds, and no double-spending. Once validated, the transaction is grouped with other verified transactions into a "block."
-
Block Creation and Adding:
Once validated, transactions are grouped into a block and added to the blockchain. This block is securely linked to the previous block through cryptographic hashes, creating an immutable chain of blocks.
-
Distribution:
The updated blockchain is distributed across the network. All nodes store a copy of the blockchain, ensuring transparency and preventing tampering or discrepancies.
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that securely records and stores transactions across a network of computers, ensuring data integrity, transparency, and immutability.
Transaction Creation
A transaction, whether a cryptocurrency transfer or smart contract execution, is represented as a "block" of data containing essential information. The data is hashed and prepared for validation before being added to the blockchain.
Verification and Consensus
Before adding a transaction to the blockchain, it must be verified through consensus mechanisms such as:
-
Proof of Work (PoW): Miners solve complex puzzles to validate transactions, ensuring network security through computational effort.
-
Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on the cryptocurrency they stake, making this method energy-efficient and secure.
-
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Stakeholders vote for delegates who validate transactions, improving speed and scalability.
-
Proof of Authority (PoA): Trusted validators efficiently validate transactions, suitable for private blockchains.
-
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): Used in permissioned blockchains, PBFT ensures consensus despite malicious or faulty nodes.
Adding to the Blockchain
Verified blocks are added to the blockchain in chronological order, linked cryptographically to ensure immutability. Altering a block would require changing every subsequent block, making tampering infeasible.
Decentralized and Transparent Ledger
Each participant maintains a copy of the blockchain, ensuring transparency and security. Discrepancies are automatically rejected by the network, preventing unauthorized modifications.
Security through Cryptography
Blockchain uses cryptographic hashing to secure data. Any alteration disrupts the chain, making tampering detectable. This ensures the integrity and security of the blockchain.
Execution and Validation
Blocks added to the blockchain are immutable, ensuring transparency and trust. The decentralized system relies on consensus mechanisms for security and accountability.